[Originally published as Bacteria Evolution]
The shape of bacteria has long been anticipated to correlate with movement. From an evolutionary perspective, form is predicted to follow function – but, it had yet to be tested. In the words of evolutionary geneticist Fouad El baidouri, “despite a few pioneering attempts to link bacterial form and function, functional morphology is largely unstudied in prokaryotes [bacteria].”
Now a landmark study has been published in Nature, Ecology & Evolution by a research team lead by El baidouri from the University of Lincoln in the United Kingdom. Elizabeth Allen explains in Phys Org,
The shape of bacteria does not influence how well they can move – this is the surprising finding… The findings refute long-held theories that there should be a strong link between the evolution of shape in bacteria and their ability to move.
Evolutionary Prediction
El baidouri’s research team studied 325 different species of Firmicutes bacteria to address a scientific gap between the knowledge about the evolution of shape in single-cell organisms, like bacteria, and their resulting differences in motility, and their potential to cause infectious diseases—pathogenicity.
“Many evolutionary biologists have asked why animals are shaped the way they are, but until now the scientific community has relied on mathematical models to predict the relationship between shape and movement in bacteria,” Humphries explained.
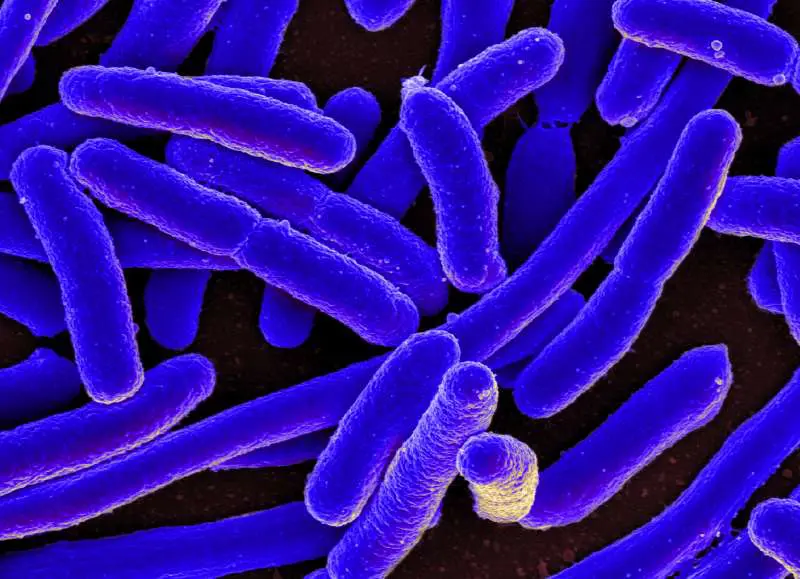
“We expected swimming bacteria,” Humphries continued in an interview with Allen, “to be rod-shaped [e.g. pictured top—E. coli] in order to reduce their energy costs, but experimental tests are rare and, surprisingly, analyses of this relationship in an evolutionary context are lacking entirely.”
The team’s publication, entitled “Independent evolution of shape and motility allows evolutionary flexibility in Firmicutes bacteria,” argued in the paper’s abstract that –
“One clear and recurring [evolutionary] prediction for form and function in microorganisms in general is that shape and motility are correlated.”
Predictions Don’t Match Observations
Contrary to these form and function predictions, however, “Our research,” Humphries continued in an interview published in ScienceDaily, “has produced evidence that these theoretical predictions don’t match reality, at least in this group of bacteria, and it therefore makes a major contribution to our understanding of the evolution of bacteria.”
“We fully expected to confirm a widely-held belief,” explained El baidouri, “backed by strong theoretical predictions, that rod-shaped cells would move more effectively than coccoid (pictured left – Staphylococcus) cells, and that shape and motility had co-evolved. We used a number of approaches to confirm our findings, and to our great surprise we didn’t find any association between the two traits.”
The team findings ran counter to predictions formulated by the current prevailing theory of evolution—the modern synthesis theory of evolution, also known as neo-Darwinism. “In contrast to clear predictions from [evolutionary] theory,” the team reported, “we show that cell shape and motility are not coupled… We find no association between shape and lifestyle [motility], and contrary to recent evidence, no indication that shape is associated with pathogenicity.”
Findings Falsify Theory
“One of the most useful properties of scientific theories,” the US National Academy of Science notes, “is that they can be used to make predictions about natural events or phenomena that have not yet been observed.” The theory of evolution, therefore by definition, since it clearly failed as a predictor of observed natural events, is falsified as a scientific theory.
The validity of the theory of evolution has been under increasing constant pressure over the last several decades as more investigative tools have become available—specifically, in association with the emergence of the genomic revolution during the late twentieth century.
Most recently, there has been increasing pressure to recognize that the theory may have reached a tipping point. An increasing number of evolutionary biologists have published articles and books critical of the current theory of evolution over the past ten years – dividing the evolution industry into irreconcilable factions. One of the most recent books includes Robert Richards and Michael Ruse’s Debating Darwin (2016) published by the University of Chicago.
Pathway to New Theory
In 2016, in an effort to address problems and redesign a united pathway to a new theory of evolution, the Royal Society convened a conference of leading evolutionary scientists entitled “New trends in evolutionary biology: biological, philosophical and social science perspectives.” According to the Royal Society,
Developments in evolutionary biology and adjacent fields have produced calls for revision of the standard theory of evolution, although the issues involved remain hotly contested.
Achieving a consensus on a revised theory of evolution, like El baidouri’s shape of bacteria research project, did not reach the intended goal. Amazingly, even though 1) evolution in the media is presented as a fact; 2) the three-day conference with several hundreds of today’s major evolution advocates were in attendance; and 3) the conference was open to the media—not a single major news organization reported on the event. Media bias is blatant—burying even scientific facts.
Conference attendees, Paul Nelson and David Klinghoffer, senior fellows at the Discovery Institute, in the article “Scientists Confirm: Darwinism Is Broken” published by CNS News a few weeks later in December explains:
Darwinian theory is broken and may not be fixable. That was the takeaway from a meeting last month organized by the world’s most distinguished and historic scientific organization, which went mostly unreported by the media.
Science writer Carl Zimmer in The Atlantic in the article,
“The biologists who want to overhaul evolution, a half-century’s worth of scientific discoveries since the last major update to evolutionary theory has some researchers pushing for a paradigm shift,” quotes Kevin Laland, one of the event organizers early during the convention, took the high-road sensing the tension –
“I think it’s going quite well. It hasn’t gone to fisticuffs yet.”
Money and Fame
In getting to what is really happening within the evolution industry, Jerry Coyne of the University of Chicago and author of the book “Why Evolution is True” – who did attend the meeting – said in an unseemly candid moment,
Maybe sometime a New Paradigm will come around, but this isn’t it. The noise we heard from London, outside of a few papers by people like Futuyma, is the noise of Templeton’s prize horses jockeying for money and fame.
The driving force of the evolution industry centers on “jockeying for money and fame”—not science. Even though the evidence uncovered investigating the shape of bacteria evolution clearly falsifies the theory of evolution, the ties to “money and fame,” for many in the industry, paralyzes simple logic.
Genesis
Despite a flood of challenges since the publication of The Origin of Species in 1859 by Charles Darwin followed by more than 150 years of unprecedented efforts in the history of mankind to prove otherwise, the scientific evidence continues to be compatible with the Genesis record written by Moses.
Louis Pasteur, a French chemist and microbiologist renowned for his discoveries of the principles of vaccination, microbial fermentation, and pasteurization developed vaccines for Rabies, Diphtheria, Anthrax and is credited for disproving the doctrine of spontaneous generation – as advocated by Darwin.
The more I study nature the more I stand amazed at the work of the Creator.
Evolution, once a theory in crisis, is now in crisis without even a cohesive unifying theory.
Biological evolution exists only as a philosophy, not a science.