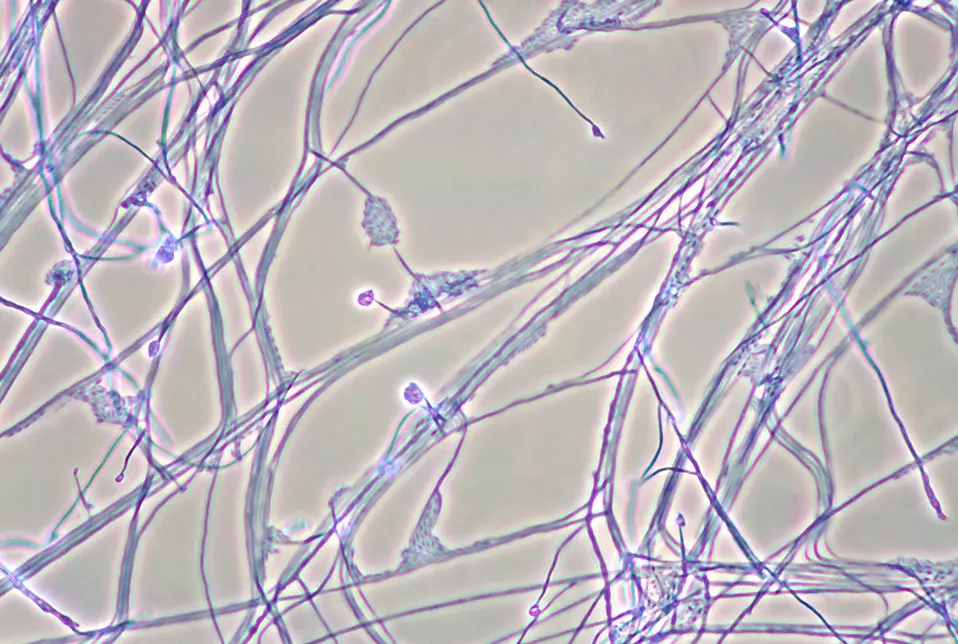
Photomicrograph of the modern fungus Acremonium recifei
[Originally published as Ancient Fungal Clues]
Fungal clues recently discovered off the coast of South Africa further stretch the boundaries of the theory of evolution. Birger Rasmussen, a geology professor at the Western Australian School of Mines, was drilling at a depth of 2,600 feet. His goal was to date the ancient submarine lava in the Ongeluk Formation assumed to be 2.4 billion years old in Northern Cape Province of South Africa, but then he unexpectedly noticed what appeared to be microfilaments .
“I was startled to find a dense mesh of tangled fossilized microbes,” Rasmussen said in an interview with LiveScience.
To Phys.org, Rasmussen recalled that, “My attention was drawn to a series of petrified gas bubbles, and when I increased the magnification of the microscope, I was startled.” The bubbles were “filled with hundreds of exquisitely preserved filaments that just screamed ‘life.’”
Indistinguishable
To gain a biological perspective, Rasmussen solicited the help of Stefan Bengtson, a paleobiologist at the Nordic Center for Earth Evolution at the Swedish Museum of Natural History. Bengston told Redfern:
“[The fossils] are practically indistinguishable in habitus and habitat from the proven fungi in the much younger fossil record… We were quite excited that the fossils were so fungus-like.”
Helen Briggs, a BBC science writer, in the article “’World’s oldest fungus’ raises evolution questions,” agreed:
“The fossils, drilled from rocks that were once beneath the seafloor, resemble living fungi.”
Redfern’s ancient fungi discovery of what appear to be “living fossils,” a term coined by Charles Darwin in The Origin of Species yet disdained by the evolution industry, upends contemporary evolution origin of life theories in many ways—beginning with the issue of dating fossils.
Dating
The estimated dating of the fossils pushes the limits of contemporary evolutionary estimates. “Scientists say,” Briggs reports, “the discovery could push back the date for the oldest fungi by one to two billion years.” Changing the origin of a multicellular organism date by two billion years is no small deal, since previous radiometric dating assumptions estimates the age of the Earth without any organisms to be just 4.4 billion years old.
“If the research holds, it would dramatically change “our sense of the timetable of evolutionary history,” explained Andrew H. Knoll, Fisher Professor of Natural History at Harvard University in an interview with Redfern.
Rasmussen’s finding is now forcing evolution scientists to rethink the origin of life timeline. “Up until now,” as Dockrill explains, “previous geological evidence for fungi only extended as far back as 385 million years ago, but the fossilized traces of microscopic creatures found in the volcanic rock were a whole 2 billion years older.” This is not a trivial issue, with far-reaching implications.
“The finding could reset the spacing of some of the earliest branches on the tree of life,” Dockrill acknowledges.
Why it’s so Startling
A fungus is a eukaryote organism belonging to the animal and plant kingdoms. At the cellular level, eukaryotes are multicellular with a cell membrane and a nucleus in each cell. No one believes life started naturally with eukaryotes.
The current consensus of contemporary evolutionary scientists is that eukaryotes evolved from prokaryotes. Prokaryotes, like eukaryotes, have a cell membrane but lack more complex cellular structures, including a nuclei and mitochondria within the cell.
The evolution of a prokaryote cell to a more complex organism, however, is far from trivial with the evolutionary steps imagined being more speculative than ever. Somehow, according to the University of California, Berkley Understanding Evolution article entitled “From Prokaryotes to Eukaryotes” they have to believe:
“Eukaryotics…. [are] the great-great-great-great-great-great-great-great-great granddaughter of a free-living bacterium.”
Whatever the evolutionary steps, unknown gaps of time must have elapsed for eukaryotes to evolve from prokaryotes through Darwin’s “slight, successive changes.”
But with estimates pushing the origin of prokaryotes to 3.5 billion years ago, scientists eventually will have to face the consequences of this re-setting of the timeframe for the origin of life.
Skeptical of the re-setting, Doug Erwin, curator at the Smithsonian National Museum of Natural History, in an interview with Redfern pin-pointed a problem:
“[The origin of life] would significantly precede fossil evidence and molecular clock analysis for the origin of eukaryotes, much less the origin of fungi.”
The plot thickens: the seemingly continuous cycle of re-setting the origin of life date to progressively earlier times places the validity of some of the evolution industry’s most popular theories in jeopardy.
Oxygen
In 1952, Nobel prize-winning chemist, Harold Urey, published the book entitled “The Planets: Their Origin and Development.” He speculated that Earth’s early atmosphere was probably like interstellar gases composed of ammonia, methane, and hydrogen—a reducing atmosphere containing no oxygen. Urey named the natural mechanism of his theory cosmochemistry.
In testing the new theory, Urey’s graduate student, Stanley Miller, produced in a laboratory model measurable quantities of simple amino acids – life’s protein building blocks. Now known as the Miller-Urey experiment, the evidence seemed, at least in part, to validate Urey’s cosmochemistry theory.
Oxygen, according to the theory, was eventually produced and released into Earth’s atmosphere through the metabolic activity of microbes on a massive scale. Through a yet unknown natural phenomenon, a variety of microbe somehow acquired an enzyme to convert carbon dioxide into oxygen driven by light from the sun.
Photosynthesis is the name of this metabolic reaction and the only class of bacteria known that fits this requirement is the Cyanobacteria. Their supposed massive release of oxygen into the Earth’s atmosphere has been called the Great Oxygen Event.
This prokaryotes, according to the theory, produced and released the third most abundant chemical element in the universe by weight and the most abundant chemical element in the Earth’s biosphere, air, sea, and land – no small project for a colony of little prokaryotes.
If ancient fungal clues re-set the dating of the emergence of eukaryotes, Rasmussen explains:
“This would have tremendous implications for the lifestyle of the early ancestors of eukaryotes and fungi.”
Marlowe Hood in the PhysOrg article entitled ”Fossils may be earliest known multicellular life: study,” April 2017, explains the game-changing oxygen problem:
“The new dating meant that not only had these fungus-like creatures lived in a dark and cavernous world devoid of light, but they also lacked oxygen.”
Fungi, including marine fungi, however, must have free oxygen to survive. Unlike plants, fungi must get their energy from living off of dead plants and other fungi. So, the lack of oxygen along with the lack of an environment rich in organic material invalidate the probability of the estimated time of origin.
Dating Assumptions
Executive director of the National Center for Science Education, Eugenie Scott, explains in the book Evolution vs Creationism the problem with ascribing to assumptions based on assumptions:
“If certain assumptions are made about it [radiometric dating], then, it can yield a date which could be called the apparent age. Whether or not the apparent age is the true age depends completely on the validity of the assumptions.”
Clues
The ancient fungal clues challenge the evolutionary theory in two highly significant ways. Evidence for Darwin’s highly anticipated “slight successive changes” has not been observed even if given a range of billions of years. Or in other words, the fossils show:
Once a fungi, always a fungi.
The apparent radiometric dating, secondly, is a catch-22 problem: the origin of fungi occurs prior to the evolution industry’s popular Great Oxygen Event theory.
Fungi without oxygen = a biological impossibility
Galileo Galilei, An Italian astronomer, physicist, engineer, philosopher, and mathematician who played a major role in the scientific revolution during the Renaissance, Galileo Galilei known as the “father of observational astronomy” and the “father of modern physics declares:
“God is known by nature in his works, and by doctrine in his revealed word.”
Genesis
Despite a flood of challenges since the publication of The Origin of Species followed by more than 150 years of unprecedented scientific efforts in the history of science to prove otherwise, the evidence in nature is increasingly best explainable by the Genesis record written by Moses.
Evolution, once a theory in crisis, is now in crisis without a unifying theory or reproducible scientific evidence.
Biological evolution exists only as a philosophy, not a science.